8. BLE¶
8.1. Overview¶
Features supported by BLE:
- Bluetooth HOST features
Roles supported by GAP: Peripheral and Central, Observer and Broadcaster
Roles supported by GATT: Server and Client
Support pairing including the secure connection feature in Bluetooth 4.2
Support permanent storage of Bluetooth specific settings and data
- Bluetooth mesh features
Supports Relay, Friend Node, Low-Power Node (LPN) and GATT Proxy roles
Support two Provisioning bearers (PB-ADV & PB-GATT)
BLE protocol stack architecture:
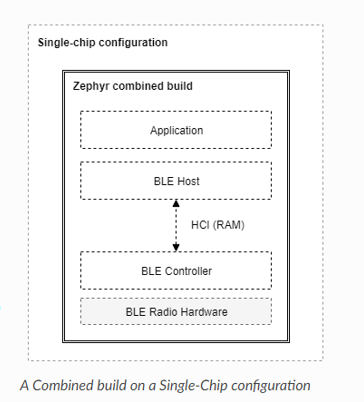
There are a total of 3 main layers, which together form a complete Bluetooth low energy protocol stack:
Host
This layer is located under the application and consists of multiple (non-real-time) networks and transport protocols, enabling the application to communicate with peer devices in a standard and interoperable manner.
Controller
The controller implements the link layer (LE LL), which is a low-level real-time protocol that provides standard interoperability for air communication together with radio hardware. LL handles the reception and transmission of packets, guarantees data transmission, and handles all LL control procedures.
Radio Hardware
Realize the required analog and digital baseband functional blocks, allowing the link layer firmware to transmit and receive in the 2.4GHz band of the spectrum.
Master Host:
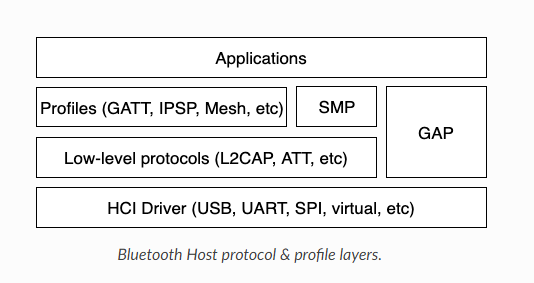
The Bluetooth Host layer implements all high-level protocols and configuration files, the most important thing is that it provides high-level APIs for applications:
HCI (Host and Controller Interface)
L2CAP (Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol)
GATT (Generic Attribute Profile)
GAP (Generic Access Profile)
SMP (Security Manager Specification)
Application:
The application layer is where users develop actual Bluetooth applications, including the necessary protocol stack parameter settings and the calling of various functions. We analyze the two devices from Bluetooth slave and Bluetooth master.
- Bluetooth slave
Initialization of related hardware and basic services
Set broadcast parameters: broadcast data, broadcast interval, scan response and other parameters or data
Profile settings: add slave services, characteristic values, and set callback functions for receiving host data, etc.
Set pairing parameters (optional)
Start the broadcast and start running
Waiting for related events, and event processing, such as receiving data from the host, being linked, etc.
- Bluetooth host
Initialization of related hardware and basic services
Set scan parameters
Set connection parameters
Set pairing parameters (optional)
Start the protocol stack and start running
Wait for related events and event processing, such as scan events, Notify events from slaves, etc.
8.2. API reference¶
API introduction.
void ble_controller_init(uint8_t task_priority)
/**
* function controller layer initialization
* @param[in] task_priority: task priority
* @return empty
*/
int hci_driver_init(void)
/**
* function HCI interface driver initialization
* @param[in] empty
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_enable(bt_ready_cb_t cb)
/**
* function Ble enable
* @param[in] cb: Call the callback function if successful
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_adv_start(const struct bt_le_adv_param *param,const struct bt_data *ad, size_t ad_len,const struct bt_data *sd, size_t sd_len)
/**
* function enable BLE broadcast
*
* @param[in] param: pointer to broadcast configuration parameter
* @param[in] ad: Pointer to the data in the broadcast packet
* @param[in] ad_len: the length of the data in the broadcast packet
* @param[in] sd: Pointer to scan response packet data
* @param[in] sd_len: scan response packet data length
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_adv_update_data(const struct bt_data *ad, size_t ad_len,const struct bt_data *sd, size_t sd_len)
/**
* function update BLE broadcast data
* @param[in] ad: Pointer to the data in the broadcast packet
* @param[in] ad_len: the length of the data in the broadcast packet
* @param[in] sd: Pointer to scan response packet data
* @param[in] sd_len: scan response packet data length
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_adv_stop(void)
/**
* function stop BLE broadcast
* @param[in] empty
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_scan_start(const struct bt_le_scan_param *param, bt_le_scan_cb_t cb)
/**
* function to enable BLE scanning
* @param[in] param: pointer to scan parameter
* @param[in] cb: scan callback function
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_scan_stop(void)
/**
* function stop BLE scanning
* @param[in] empty
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_whitelist_add(const bt_addr_le_t *addr)
/**
* function Add the device to the whitelist by address
* @param[in] addr: pointer to the address of the device to be added
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_whitelist_rem(const bt_addr_le_t *addr)
/**
* function remove the device from the whitelist
* @param[in] addr: pointer to the address of the device to be removed
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_whitelist_clear(void)
/**
* function Clear the whitelist list
* @param[in] empty
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_set_chan_map(u8_t chan_map[5])
/**
* function set (LE) channel mapping
* @param[in] chan_map: channel array
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_unpair(u8_t id, const bt_addr_le_t *addr)
/**
* function clear pairing information
* @param[in] id: Local ID (mostly just the default BT ID)
* @param[in] addr: remote device address, NULL or BT_ADDR_LE_ANY to clear all remote devices
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_conn_get_info(const struct bt_conn *conn, struct bt_conn_info *info)
/**
* function Get the information of the currently connected device
* @param[in] conn: pointer to the current connection
* @param[in] info: Pointer to the current connected device information
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_conn_get_remote_dev_info(struct bt_conn_info *info)
/**
* function Get the information of the connected device
* @param[in] info: Pointer to the current connected device information
* @return the number of connected devices
*/
int bt_conn_le_param_update(struct bt_conn *conn,const struct bt_le_conn_param *param)
/**
* function update connection parameters
* @param[in] conn: pointer to the current connection
* @param[in] param: pointer to connection parameter
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_conn_disconnect(struct bt_conn *conn, u8_t reason)
/**
* function disconnect the current connection
* @param[in] conn: pointer to the current connection
* @param[in] reason: the reason for disconnecting the current connection
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
struct bt_conn *bt_conn_create_le(const bt_addr_le_t *peer,const struct bt_le_conn_param *param)
/**
* function to create a connection
* @param[in] peer: The pointer of the device address that needs to be connected
* @param[in] param: pointer to connection parameter
* @return Success: a valid connection object, otherwise it fails
*/
int bt_conn_create_auto_le(const struct bt_le_conn_param *param)
/**
* function to automatically create devices in the whitelist
* @param[in] param: pointer to connection parameter
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_conn_create_auto_stop(void)
/**
* function Stop automatically creating devices in the whitelist of connections
* @param[in] empty
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_set_auto_conn(const bt_addr_le_t *addr,const struct bt_le_conn_param *param)
/**
* function automatically creates and connects remote equipment
* @param[in] addr: remote device address pointer
* @param[in] param: pointer to connection parameter
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
struct bt_conn *bt_conn_create_slave_le(const bt_addr_le_t *peer,const struct bt_le_adv_param *param)
/**
* function initiates a directed broadcast packet to the remote device
* @param[in] peer: pointer of remote device address
* @param[in] param: pointer to broadcast parameters
* @return Success: a valid connection object, otherwise it fails
*/
int bt_conn_set_security(struct bt_conn *conn, bt_security_t sec)
/**
* function to set the connection security level
* @param[in] conn: pointer to the connection object
* @param[in] sec: security level
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
bt_security_t bt_conn_get_security(struct bt_conn *conn)
/**
* function Get the security level of the current connection
* @param[in] conn: pointer to the connection object
* @return security level
*/
u8_t bt_conn_enc_key_size(struct bt_conn *conn)
/**
* function Get the size of the encryption key of the current connection
* @param[in] conn: pointer to the connection object
* @return the size of the encryption key
*/
void bt_conn_cb_register(struct bt_conn_cb *cb)
/**
* function Register connection callback function
* @param[in] cb: connection callback function
* @return empty
*/
void bt_set_bondable(bool enable)
/**
* function Set/clear the binding flag in the SMP pairing request/response data authentication request
* @param[in] enable: 1, enable, 0: disable
* @return empty
*/
int bt_conn_auth_cb_register(const struct bt_conn_auth_cb *cb)
/**
* function registration authentication callback function
* @param[in] cb: callback function pointer
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_conn_auth_passkey_entry(struct bt_conn *conn, unsigned int passkey)
/**
* function reply with key
* @param[in] conn: connection object pointer
* @param[in] passkey: the key entered
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_conn_auth_cancel(struct bt_conn *conn)
/**
* function cancel the authentication process
* @param[in] conn: connection object pointer
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_conn_auth_passkey_confirm(struct bt_conn *conn)
/**
* function If the password matches, reply to the other party
* @param[in] conn: pointer to the connection object
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_conn_auth_pincode_entry(struct bt_conn *conn, const char *pin)
/**
* function reply with PIN code
* @param[in] conn: pointer to the connection object
* @param[in] pin: pointer of PIN code
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_le_read_rssi(u16_t handle,int8_t *rssi)
/**
* function read the RSSI value of the other party
* @param[in] handle: the handle value of the connection
* @param[in] rssi: pointer to rssi
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_get_local_address(bt_addr_le_t *adv_addr)
/**
* function read the address of the machine
* @param[in] adv_addr: pointer to address
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
int bt_set_tx_pwr(int8_t power)
/**
* function to set the local transmit power
* @param[in] power: power value
* @return 0: success, !=0: failure
*/
8.3. Data structure reference¶
bt_le_adv_paramdata structure:
/** LE Advertising Parameters. */
struct bt_le_adv_param {
/** Local identity */
u8_t id;
/** Bit-field of advertising options */
u8_t options;
/** Minimum Advertising Interval (N * 0.625) */
u16_t interval_min;
/** Maximum Advertising Interval (N * 0.625) */
u16_t interval_max;
#if defined(CONFIG_BT_STACK_PTS)
u8_t addr_type;
#endif
};
This data structure is used to configure broadcast parameters, including local identification id, broadcast option bit field, broadcast gap, etc. The broadcast option bit field has the following enumerated type parameters to choose from:
enum {
/** Convenience value when no options are specified. */
BT_LE_ADV_OPT_NONE = 0,
/** Advertise as connectable. Type of advertising is determined by
* providing SCAN_RSP data and/or enabling local privacy support.
*/
BT_LE_ADV_OPT_CONNECTABLE = BIT(0),
/** Don't try to resume connectable advertising after a connection.
* This option is only meaningful when used together with
* BT_LE_ADV_OPT_CONNECTABLE. If set the advertising will be stopped
* when bt_le_adv_stop() is called or when an incoming (slave)
* connection happens. If this option is not set the stack will
* take care of keeping advertising enabled even as connections
* occur.
*/
BT_LE_ADV_OPT_ONE_TIME = BIT(1),
/** Advertise using the identity address as the own address.
* @warning This will compromise the privacy of the device, so care
* must be taken when using this option.
*/
BT_LE_ADV_OPT_USE_IDENTITY = BIT(2),
/** Advertise using GAP device name */
BT_LE_ADV_OPT_USE_NAME = BIT(3),
/** Use low duty directed advertising mode, otherwise high duty mode
* will be used. This option is only effective when used with
* bt_conn_create_slave_le().
*/
BT_LE_ADV_OPT_DIR_MODE_LOW_DUTY = BIT(4),
/** Enable use of Resolvable Private Address (RPA) as the target address
* in directed advertisements when CONFIG_BT_PRIVACY is not enabled.
* This is required if the remote device is privacy-enabled and
* supports address resolution of the target address in directed
* advertisement.
* It is the responsibility of the application to check that the remote
* device supports address resolution of directed advertisements by
* reading its Central Address Resolution characteristic.
*/
BT_LE_ADV_OPT_DIR_ADDR_RPA = BIT(5),
/** Use whitelist to filter devices that can request scan response
* data.
*/
BT_LE_ADV_OPT_FILTER_SCAN_REQ = BIT(6),
/** Use whitelist to filter devices that can connect. */
BT_LE_ADV_OPT_FILTER_CONN = BIT(7),
};
If you need to send a broadcast packet, the configuration can be as follows:
param.id = 0;
param.options = (BT_LE_ADV_OPT_CONNECTABLE | BT_LE_ADV_OPT_USE_NAME | BT_LE_ADV_OPT_ONE_TIME);
param.interval_min = 0x00a0;
param.interval_max = 0x00f0;
bt_dataData structure:
struct bt_data {
u8_t type;
u8_t data_len;
const u8_t *data;
};
This data structure is used to fill the data in the broadcast packet, the specific data packet type can refer to the following:
Service UUID
Local Name
Flags
Manufacturer Specific Data
TX Power Level
Secure Simple Pairing OOB
Security Manager OOB
Security Manager TK Value
Slave Connection Interval Range
Service Solicitation
Service Data
Appearance
Public Target Address
Random Target Address
Advertising Interval
LE Bluetooth Device Address
LE Role
Uniform Resource Identifier
LE Supported Features
Channel Map Update Indication
Use this data structure to configure a broadcast packet data, as shown below:
struct bt_data ad_discov[] = {
BT_DATA_BYTES(BT_DATA_FLAGS, (BT_LE_AD_GENERAL | BT_LE_AD_NO_BREDR)),
BT_DATA(BT_DATA_NAME_COMPLETE, "BL602-BLE-DEV", 13),
};
bt_le_scan_paramdata structure:
/** LE scan parameters */
struct bt_le_scan_param {
/** Scan type (BT_LE_SCAN_TYPE_ACTIVE or BT_LE_SCAN_TYPE_PASSIVE) */
u8_t type;
/** Bit-field of scanning filter options. */
u8_t filter_dup;
/** Scan interval (N * 0.625 ms) */
u16_t interval;
/** Scan window (N * 0.625 ms) */
u16_t window;
};
This data structure is used to fill scan parameters, type: There are 2 types for scanning type: BT_LE_SCAN_TYPE_ACTIVE (0x01) and BT_LE_SCAN_TYPE_PASSIVE (0x00). filter_dup: 0x00, except for targeted advertisements, accept all broadcast and scan responses, 0x01, only receive broadcast and scan responses from devices in the whitelist. interval: scan interval. window: Scan window.
If the scan request is enabled, it can be configured as follows:
scan_param.type = BT_LE_SCAN_TYPE_PASSIVE
scan_param.filter_dup = 0x00
interval=BT_GAP_SCAN_SLOW_INTERVAL_1
window=BT_GAP_SCAN_SLOW_WINDOW_1
bt_le_conn_paramdata structure:
/** Connection parameters for LE connections */
struct bt_le_conn_param {
u16_t interval_min;
u16_t interval_max;
u16_t latency;
u16_t timeout;
#if defined(CONFIG_BT_STACK_PTS)
u8_t own_address_type;
#endif
};
This data structure is used to fill the connection parameters, interval_min: minimum value of the connection gap (0x0018), interval_max: maximum value of the connection gap (0x0028), latency: The maximum slave latency allowed for the connection specified as the number of connection events. timeout: connection timeout period.
Configure the data structure as follows:
interval_min=BT_GAP_INIT_CONN_INT_MIN(0x0018)
interval_max=BT_GAP_INIT_CONN_INT_MAX(0x0028)
latency=0
timeout=400
bt_conndata structure:
struct bt_conn {
u16_t handle;
u8_t type;
u8_t role;
ATOMIC_DEFINE(flags, BT_CONN_NUM_FLAGS);
/* Which local identity address this connection uses */
u8_t id;
#if defined(CONFIG_BT_SMP) || defined(CONFIG_BT_BREDR)
bt_security_t sec_level;
bt_security_t required_sec_level;
u8_t encrypt;
#endif /* CONFIG_BT_SMP || CONFIG_BT_BREDR */
/* Connection error or reason for disconnect */
u8_t err;
bt_conn_state_t state;
u16_t rx_len;
struct net_buf *rx;
/* Sent but not acknowledged TX packets with a callback */
sys_slist_t tx_pending;
/* Sent but not acknowledged TX packets without a callback before
* the next packet (if any) in tx_pending.
*/
u32_t pending_no_cb;
/* Completed TX for which we need to call the callback */
sys_slist_t tx_complete;
struct k_work tx_complete_work;
/* Queue for outgoing ACL data */
struct k_fifo tx_queue;
/* Active L2CAP channels */
sys_slist_t channels;
atomic_t ref;
/* Delayed work for connection update and other deferred tasks */
struct k_delayed_work update_work;
union {
struct bt_conn_le le;
#if defined(CONFIG_BT_BREDR)
struct bt_conn_br br;
struct bt_conn_sco sco;
#endif
};
#if defined(CONFIG_BT_REMOTE_VERSION)
struct bt_conn_rv {
u8_t version;
u16_t manufacturer;
u16_t subversion;
} rv;
#endif
};
This data structure is the current connection data structure, which includes BLE Bluetooth connection related parameters. After the connection is successful, the data structure can be called by the user.