17. UART_echo¶
17.1. Overview¶
This example explains the process of sending received data back to the sender via UART1.
17.2. Usage Steps¶
Prepare a
USB to TTLcable, and configure theuartin the SDK directory atbl_iot_sdk/tools/flash_tool/bl602/device_tree/bl_factory_params_evb_40M.dts. For this, refer to the following example configuration.
uart {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
uart@4000A000 {
status = "okay";
id = <0>;
compatible = "bl602_uart";
path = "/dev/ttyS0";
baudrate = <2000000>;
pin {
rx = <7>;
tx = <16>;
};
feature {
tx = "okay";
rx = "okay";
cts = "disable";
rts = "disable";
};
};
uart@4000A100 {
status = "okay";
id = <1>;
compatible = "bl602_uart";
path = "/dev/ttyS1";
baudrate = <115200>;
pin {
rx = <3>;
tx = <4>;
};
feature {
tx = "okay";
rx = "okay";
cts = "disable";
rts = "disable";
};
};
};
- Steps to use:
- Connect the board's ``gpio3`` and ``gpio4`` and ``GND`` to the ``TXD``, ``RXD``, and ``GND`` of the ``USB to TTL`` serial cable, respectively.
- Compile ``customer_app/sdk_app_uart_echo`` and flash the image.
- Open two serial terminal windows (A and B, respectively), with the Baud rate for A set to 115200, and the Baud rate for B set to2000000. After powering on the board, you can see that window A has received ``1234567890abcdefg``, while window B is stuck at ``send case``. You can continue the program by typing ``1234567890abcdefg`` in window A (note that there is no echo), after which B should continue to ``recv case`` and ``end``.
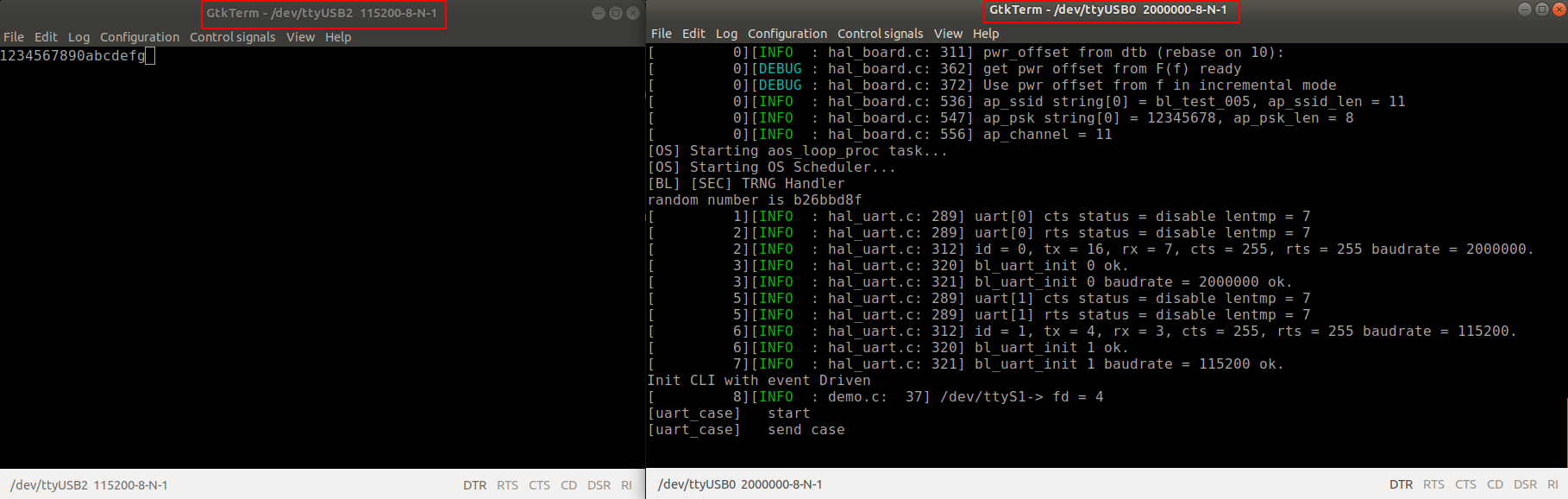
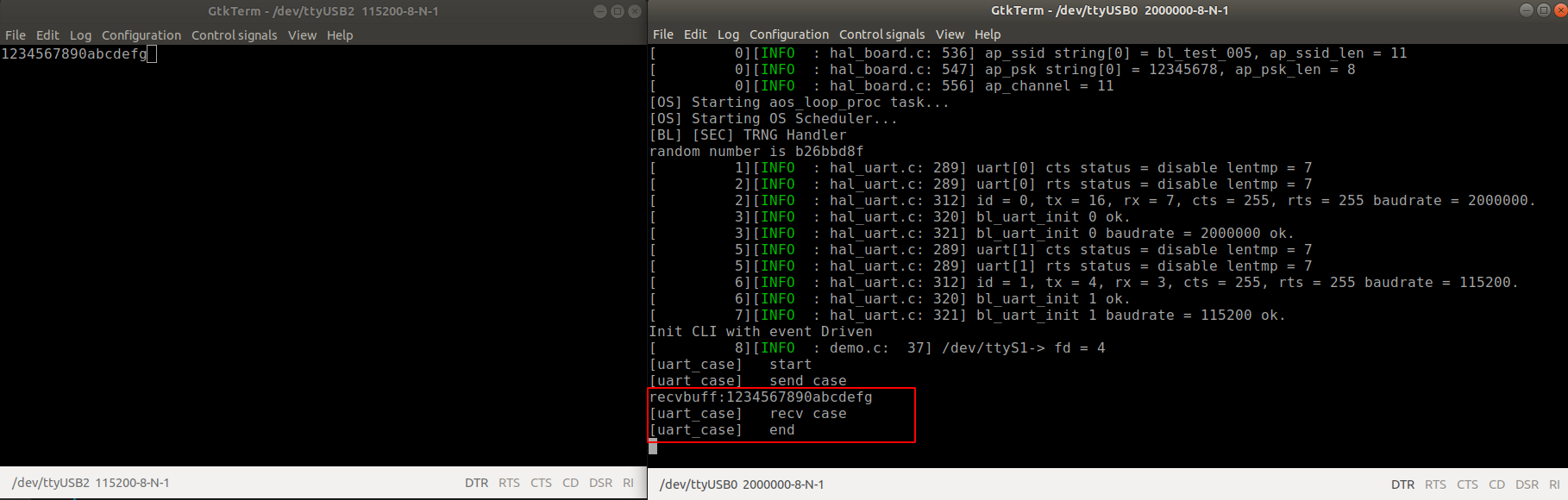
17.3. Code Examples¶
Use
aos_write()to send data to the terminal using UART1, and then wait terminal to return the received data. Upon receiving the same data as the one sent, the log port will print the contents of the message.
aos_write(fd, send_recv_log, strlen(send_recv_log));
log_step(ci_table_step_send);
while (1) {
length = aos_read(fd, buf_recv, strlen(send_recv_log));
if (length != strlen(send_recv_log)) {
continue;
}
if (memcmp(buf_recv, send_recv_log, strlen(send_recv_log)) == 0) {
printf("recvbuff:%s\r\n", send_recv_log);
log_step(ci_table_step_recv);
break;
}
vTaskDelay(10);
}
log_step(ci_table_step_end);
In
static void aos_loop_proc(void *pvParameters)atcustomer_app/sdk_app_uart_echo/sdk_app_uart_echo/main.c, ci_loop_proc is called to create theuart_echotask.