10. BLE¶
10.1. Overview¶
This example explains how to use Bluetooth Low-Energy.
10.2. Usage Steps¶
Compile and flash
customer_app/bl602_demo_eventorcustomer_app/bl702_demo_event.Use
stack_blecommand to inialize the BLE stack. Example logs:
Use
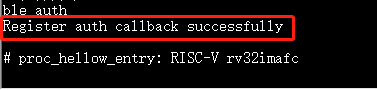
ble_initandble_authrespectively to initialize BLE and configure authentication.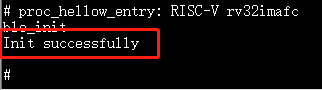
Use
ble_start_adv 0 0 0x80 0x80to enable BLE.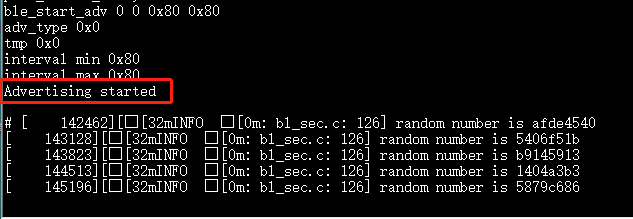
The BLE station should now be visible on nearby devices.
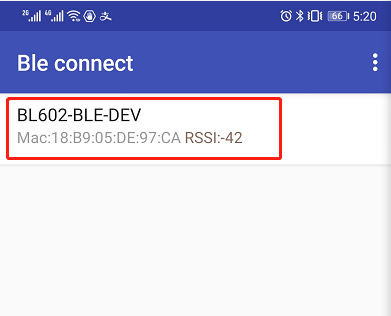
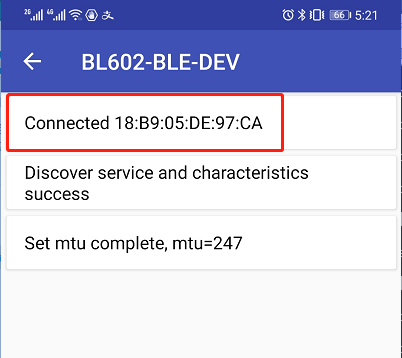
Use
ble_conn_update 0x6 0x6 0x0 0x1f4to update connection params.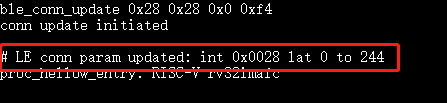
SMP pairing. Commands vary depending on the BLE security level 2 vs 3.
ble_security 2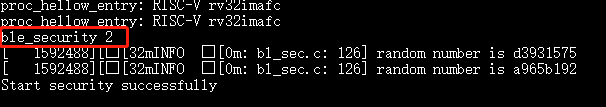
Displays
Confirm passkey for xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx (public). Use the commandble_auth_pairing_confirmto confirm pairing.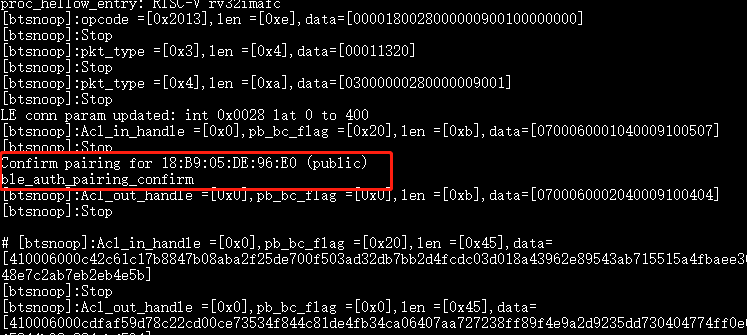
If pairing is sucessful, the console displays
Bonded with xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx (public).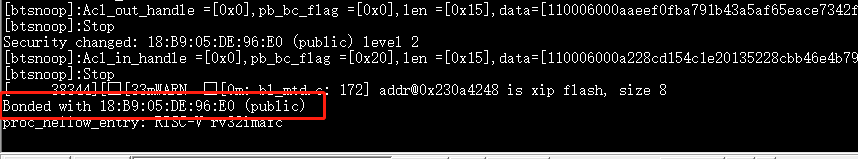
ble_security 3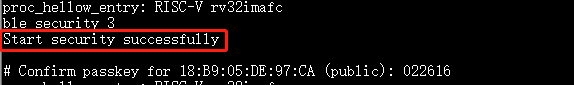
Displays
Confirm passkey for xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx (public):xxxxxx. Useble_auth_passkey_confirmto confirm pairing.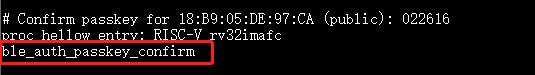
If pairing is successful, the console displays
Bonded with xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx (public)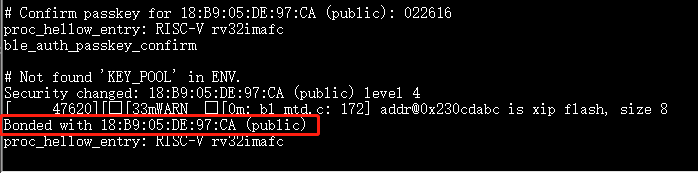
10.3. Available commands¶
10.3.1. ble_init¶
Purpose: Common BLE initialization. Required before all other BLE CLI commands.
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_init
10.3.2. ble_auth¶
Purpose:Register SMP interface.
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_auth
10.3.3. ble_unpair¶
Purpose:Clear pairing keys.
Params: 1st param indicates device address type:
0: Device is a public address.
1: Device is a random address.
2: Device is a resolvable or public address.
3: Device is a resolvable or random address.
2nd param indicates the device address in big endian.
0clears all device keys.Example:
ble_unpair 0 0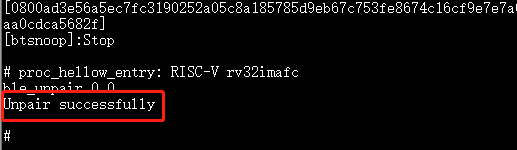
10.3.4. ble_start_adv¶
Purpose: Enable ADV broadcast.
1st param indicates broadcast type.
0:adv_ind - connectable, scannable.
1:adv_scan_ind not connectable, scannable.
2:adv_nonconn_ind not connectable or scannable.
3:adv_direct_ind connectable by limited devices, not scannable.
2nd param indicates broadcast mode.
0:General discoverable.
1:non-discoverable.
2:limit discoverable.
3rd param is the minimum broadcast gap, calculated as 0.625ms * N with a range of 20 ms to 10.24 s.
The fourth parameter is the maximum broadcast gap.
Example:
ble_start_adv 0 0 0x80 0x80
10.3.5. ble_stop_adv¶
Purpose: stop ADV broadcast.
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_stop_adv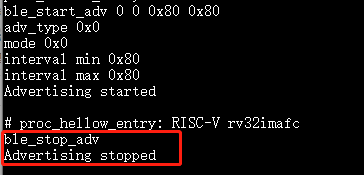
10.3.6. ble_start_scan¶
Purpose: Start scanning for broadcasting devices.
1st param is broadcast type:
0: passive scan, only monitoring for broadcasts.
1: active scan, monitoring for broadcasts and sending scan_req packets.
2nd param configures broadcast package filtering:
0: don’t filter duplicates.
1: filter duplicates.
2:only accept broadcasts and scan response packets from allowlisted devices
4: use advanced filtering strategy
3rd param is scanning gap, calculated as 0.625ms * N with a range of 20 ms to 10.24 s.
4th param is scanning window, calculated as 0.625ms * N with a range of 20 ms to 10.24 s.
Example:
ble_start_scan 0 0 0x80 0x40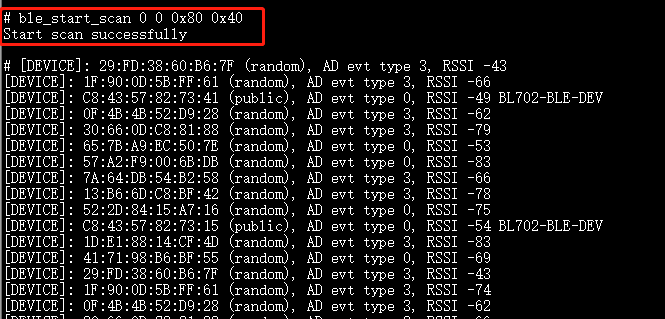
10.3.7. ble_stop_scan¶
Purpose: Stop scanning.
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_stop_scan
10.3.8. ble_conn_update¶
Purpose: update connection params
1st param is minimum connection gap, calculated as N * 1.25 ms with a range of 7.5 ms to 4 s.
2nd param is maximum connection gap.
3rd parameter indicates how many connection events are delayed from the device. The range is 0~499. For example, if the value is set to 1, it indicates that the data interaction is delayed for an event. It reduces the interaction frequency and save power.
4th param is connection timeout, calculated as N * 10 ms, with a range of 100 ms to 32 s.
Example:
ble_conn_update 0x28 0x28 0x0 0xf4
10.3.9. ble_security¶
Purpose: Set SMP encryption level.
Param: encryption level, of which are 5:
0: Only used for BR/EDR, such as SDP service.
1: No encryption is required and no authentication is required.
2: Require encryption without authentication.
3: Both encryption and authentication are required, for example, both parties need to enter a PIN code
4: Both encryption and authentication are required, and the 128bit key is passed
Example:
ble_security 2
10.3.10. ble_get_device_name¶
Purpose: Get local device name
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_get_device_name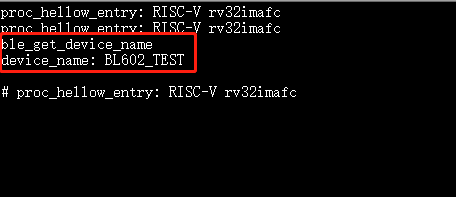
10.3.11. ble_set_device_name¶
Purpose: Set local device name
Params: local device name
Example:
ble_set_device_name bl602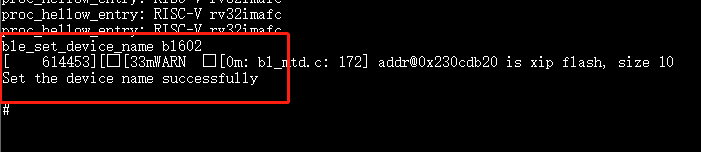
10.3.12. ble_read_local_address¶
Purpose: Read local device address
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_read_local_address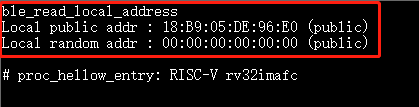
10.3.13. ble_set_adv_channel¶
Purpores: Set ADV channel
Params: ADV channel number. Range is 1-7. The size of the parameter is 1 byte. bit0 represents channel 37, bit1 represents channel 38, bit2 represents channel 39
Example:
ble_set_adv_channel 4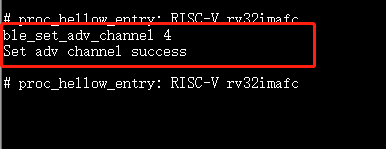
10.3.14. ble_connect¶
Purpose: Connect to the device at the specified address
Params: 1st param is the address type:
0: public device address
1: random device address
2: resolvable or public address
3: resolvable or random address
2nd param is the device address, in big endian.
Example:
ble_connect 0 18B905DE96E0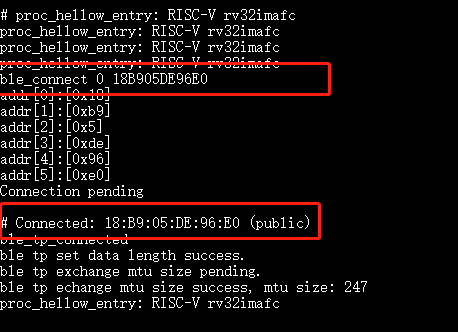
10.3.15. ble_disconnect¶
Purpose: Disconnect from device from specified address
Params: 1st param is the address type:
0: public device address
1: random device address
2: resolvable or public address
3: resolvable or random address
2nd param is the device address, in big endian.
Example:
ble_disconnect 0 18B905DE96E0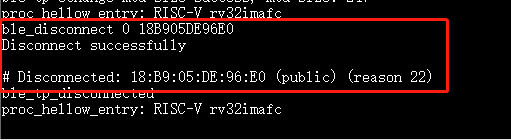
10.3.16. ble_select_conn¶
Purpose: Select a connection as the current connection from multiple connections.
0: public device address
1: random device address
2: resolvable or public address
3: resolvable or random address
2nd param is the device address, in big endian.
Example:
ble_select_conn 1 5F10546C8D83selects it as the current connection, and subsequent operations will act on that connection.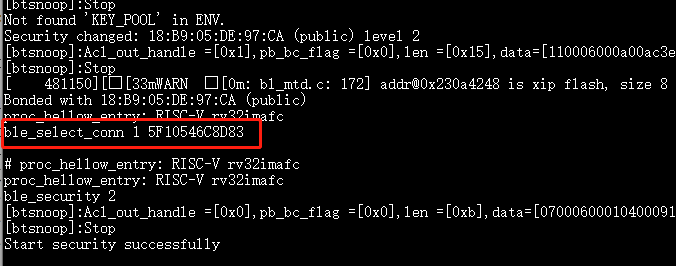
10.3.17. ble_auth_cancel¶
Purpose: cancel in-progress authentication
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_auth_cancelduring SMP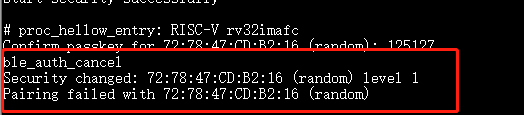
10.3.18. ble_auth_passkey_confirm¶
Purpose: Confirm receiving passkey from a remote device and proceed with pairing.
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_auth_passkey_confirmto confirm pairing during SMP with a security level of 3.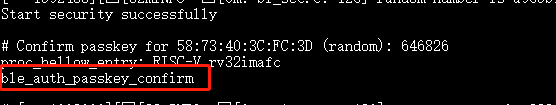
10.3.19. ble_auth_pairing_confirm¶
Purpose: Confirm receiving a pairing request from a remote device and proceed with pairing.
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_auth_pairing_confirmto confirm pairing during SMP with a security level of 2.
10.3.20. ble_auth_passkey¶
Purpose: Input authentication passkey.
Params: the value of the passkey. The range is 0-999999.
Example: When pairing with the ble_security 3 command and the SMP pairing method is PASSKEY_INPUT (Implementation: when registering the SMP interface function with ble_auth, populate the data structure bt_conn_auth_cb with the function passkey_entry filled, passkey_display and passkey_confirm unfilled, and the default values for all other fields), the serial port will prompt “Enter passkey for XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (public)”, then enter the command
ble_auth_passkey 111111to complete the pairing.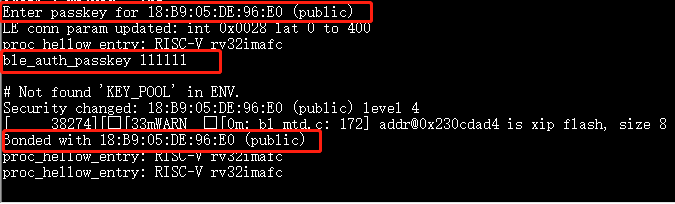
10.3.21. ble_exchange_mtu¶
Purpose: exchange MTU size
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_exchange_mtu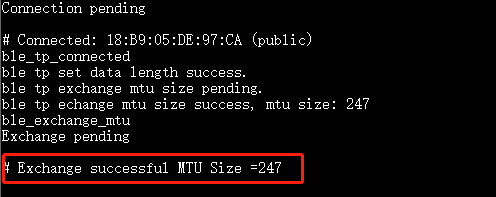
10.3.22. ble_discover¶
Purpose: look up specified service or feature.
1st param is the look-up type.
0:primary
1:secondary
2:include
3:Characteristic
4:Descriptor
2nd param is UUID of 2 bytes.
3rd param is the start handle of 2 bytes.
4th param is the end handle of 2 bytes.
Example:
ble_discover 0 0x1800 0x1 0xffffafter a successful connection.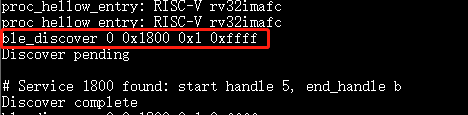
10.3.23. ble_read¶
Purpose: Read data with specified handle.
1st param is the handle of 2 bytes.
2nd param is the read offset of 2 bytes.
Example:
ble_read 0x5 0after a sucessful connection.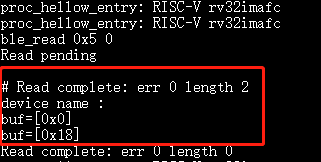
10.3.24. ble_write¶
Purpose: write data with specified handle.
1st param is the handle of 2 bytes.
2nd param is the write offset of 2 bytes.
3rd param is data length of 2 bytes, with a max value of 512.
4th param is the data to write.
Example:
ble_write 0xf 0 2 0102write 2 bytes of data after a successful connection.01is the first byte,02is the second byte.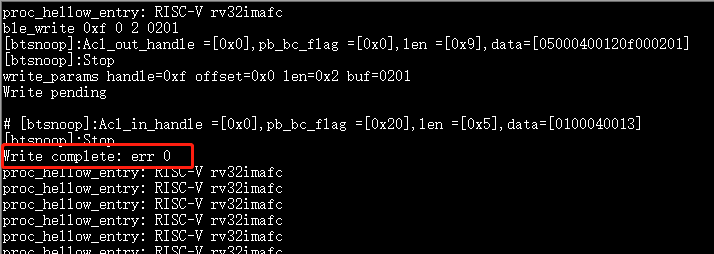
10.3.25. ble_write_without_rsp¶
Purpose: write data without requiring a reply.
1st param enables the sign write command:
0: disable sign write.
1: enable sign write.
2nd param is the handle of 2 bytes.
3rd param is data length of 2 bytes, with a max value of 512.
4th param is the data to write.
Example:
ble_write_without_rsp 0 0xf 2 0102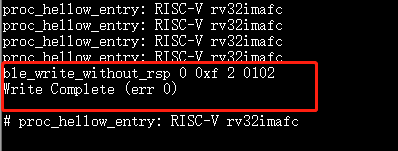
10.3.26. ble_subscribe¶
Purpose: Subscribe CCC.
1st param is the CCC handle.
2nd param is the handle of the subscription value.
3rd param is the subscription type:
1: notification
2: indication
Example:
ble_subscribe 0xf 0xd 0x1after a successful connection to enable CCC notification.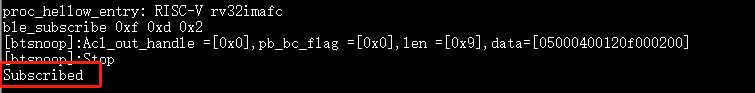
10.3.27. ble_unsubscribe¶
Purpose: Cancel CCC subscription.
Params: N/A
Example:
ble_unsubscribe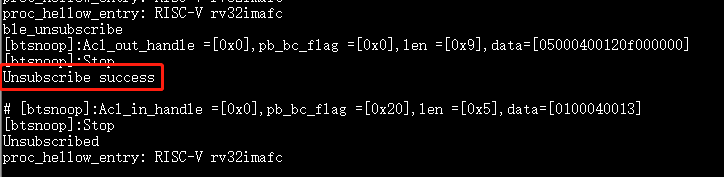
10.3.28. ble_set_data_len¶
Purpose: Set PDU data length.
1st param is the maximum length of the effective transmission payload, and the range is 0x001B-0x00FB.
2nd param is the maximum time for the transmission. The range is 0x0148-0x4290.
Example:
ble_set_data_len 0xfb 0x0848after a successful connection.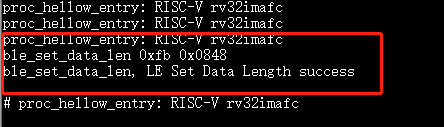
10.3.29. ble_conn_info¶
Purpose: Print out all connection information.
Param: N/A
Example:
ble_conn_infoafter a successful connection.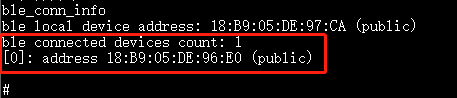
10.3.30. ble_disable¶
Purpose: disable BLE
Param: N/A
Example:
ble_disable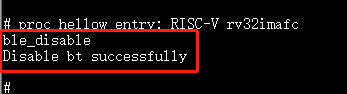
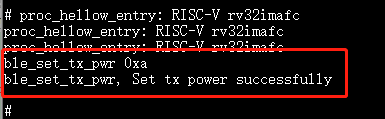
10.3.31. ble_set_tx_pwr¶
Purpose:Set TX power
Param: TX power level
Example:
ble_set_tx_pwr 0xa